“What’s a good credit score?” is a question most people have asked at least once in their life. Credit scores are issued as three-digit numbers, typically between 300 and 850. These scores are separated into five categories, very poor, fair, good, very good, and exceptional. The higher the score, the more creditworthy you are deemed to be. That means your loan amounts can be bigger and your interest rates can be lower when applying for credit.

“What’s a good credit score?” is a question most people have asked at least once in their life. It usually comes up the first time a person wants to buy a car or get a credit card. Credit scores really come into play when applying for a mortgage. Without a good credit score, obtaining a significant loan becomes much more difficult.
First of all, what is a credit score, and what does it mean? Credit scores are issued as three-digit numbers, typically between 300 and 850. They are calculated based on a number of factors gathered from a person’s credit and income history. A credit score is used by lenders as a tool to try to estimate how likely a person is to pay back a loan. The higher the score, the safer the loan. The safer the loan, the better terms a borrower is likely to get.
- What Kind of Credit Scores are Out There?
- What are the Different Categories and Ranges or Credit Scores?
- Major Credit Reporting Bureaus
- What to Do if You Don’t Have a Credit Score or Need to Raise It
What Kind of Credit Scores are Out There?
The type of credit score familiar to most people is the FICO score. It uses statistical models derived from a person’s credit history to develop the score. It established the familiar 300-850 score range.
Another type of credit score is the VantageScore. It was established as a joint venture of the three major credit bureaus (Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion). Initially, it used a different score range, but the current VantageScore 4.0 now uses the familiar 300-850 range. Its statistical models weigh types of credit issues differently. For example, the most recent version of the VantageScore weights medical debt less heavily than other kinds of debt.
What are the Different Categories of Credit Scores?
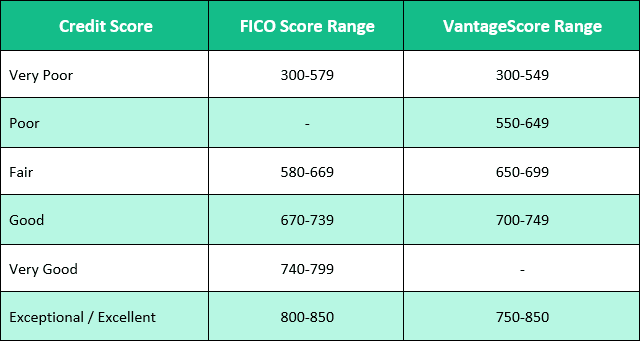
Credit scores are separated into different credit score ranges and these ranges are placed into five categories: very poor, fair, good, very good, and exceptional. The higher the score, the more creditworthy you are deemed to be. That means your loan amounts can be bigger and your interest rates can be lower when applying for credit. Having a good credit score will help you save money throughout your lifetime in the form of money paid in interest. This can really add up over time.
A low credit score can have a negative impact in a number of ways. If you have a low credit score, not only will your loan amounts be smaller with higher interest rates, but even your renting and employment opportunities can be affected. These are all really important reasons why you need to know your credit score and what you can do to raise it (if necessary).
Here is a deeper, more detailed look at what a good credit score is, and what each of the possible credit score categories means for you and your financial future.
What’s a Very Poor Credit Score?
- FICO: 300-579
- VantageScore: 300-549
- (VantageScore also has a Poor Credit Score range of 550-649)
A surprisingly high number of people (17%) have what’s considered a Very Poor credit score of 300-579. With this score, credit applicants may be required to pay a hefty fee or deposit, if they are approved at all…and there is a good chance they won’t be approved by any major bank or lending agency. This is because lenders have assessed the risk and determined a high chance that the debt will not be able to be repaid as agreed. This is especially true when competition for loans is high. When a lot of people are seeking loans, people with very poor scores are more likely to miss out.
Fortunately, there are plenty of unconventional loan agencies who work with “very poor credit” applicants to help them find a solution to their credit and loan needs. Look into companies such as Lift Credit Services who offer simple loans with easy payment schedules and a declining rate schedule.
As for mortgage applicants, being approved for a loan is still possible. However, a 10% down payment on an FHA mortgage is required for borrowers with a credit score lower than 500. Here is a tip. Since it will take more people time to save that 10% down payment, it is a good idea to use that time to also clean up credit issues. You can work on improving your credit score while saving. More on that later.
What’s a Fair Credit Score?
- FICO: 580-669
- VantageScore: 650-699
As for people with Fair credit (20%), their credit score ranges from 580-669. Applicants with scores in this range are considered “subprime” borrowers with a higher-than-normal credit risk.
What’s a Good Credit Score?
- FICO: 670-739
- VantageScore: 700-749
The majority of people (22%) have a Good credit score of 670-739. According to Fair Isaac Corporation (FICO), only 8% of borrowers in this category are likely to become seriously delinquent on their future loans. This is the minimum score range that you want to target.
What’s a Very Good Credit Score?
- FICO: 740-799
- (VantageScore doesn’t have a score range labeled Very Good)
People who are categorized as having Very Good credit (18%) maintain a 740-799 credit score. These borrowers are likely to receive better-than-average interest rates from lenders.
What’s an Exceptional Credit Score?
- FICO: 800-850
- VantageScore (this range is labeled Excellent): 750-850
At the top of the range, those (20%) who hold an exceptional credit score of 800-850 will get the best rates from lenders. This can ultimately mean a savings of literally thousands of dollars. Aiming for an Exceptional Credit Score is a good investment over time.
Multiple Sources, Multiple Scores
The U.S. has three major credit reporting bureaus (Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion) that dominate the market for collecting, analyzing, and disbursing consumer information in the credit markets. Originally serving regional markets (west, midwest, south, and east), these three companies now report across all regions of the United States and even globally.
There are dozens of smaller credit reporting agencies that serve special interest markets but when it comes to the general public, these three are the only ones with national significance.
Each major credit reporting bureau has its own determinants and calculations when assigning you a credit score. Because of this, your credit score can vary depending on which service you inquire through, even though they collect the same type of information about consumers. It is important to know each of your scores. If there is a significant difference between one of your scores and the others, that could indicate an error that is hurting your credit prospects.
The information collected by the three big agencies includes:
- Name and address
- Date of birth
- Social security number
- Credit history (debts, payment history, credit applications)
- Loan history (student loans, housing)
Factors that affect your credit score for the worse include:
- Number and severity of late payments
- High debt-to-income ratio (all your monthly debt payments divided by your gross monthly income)
- Low credit utilization rate (your credit card balance divided by your credit limit, for each card as well as altogether)
- Number of “hard” inquiries into your credit report (a potential lender reviewing your credit because you’ve applied to receive credit from them)
- Many new, recently-opened credit card accounts
- Public records (bankruptcy, civil judgments, tax liens)
Each credit reporting bureau uses all of this personal information to calculate your credit score. It is often called your FICO Score which is named for the data-analytic firm associated with the original calculation method, but now that slightly different calculation methods are used, your credit score can also be named after the agencies Equifax Credit Score, VantageScore, and TransRisk.
Because of the slightly different calculation methods used between the three bureaus along with various gaps in information-gathering and reporting, you will not always have the same score across all three bureaus.
Unfortunately, this means it is necessary for consumers to check their score with each bureau in order to check for discrepancies. Since different lenders will request your credit score from different credit reporting bureaus, it’s possible to be denied for a lower score on one report even though your score is higher on another. You should always look into scores that have a large discrepancy with the others since it could be due to an error. Staying on top of your credit is an important part of having a good credit score.
What If I Don’t Have a Credit Score or Need to Raise It?

If you are lacking any credit score whatsoever, that usually just means you don’t have any history of credit. This is often because a person is young and hasn’t had a chance to establish credit. Since credit scores don’t take this into account, it is up to you to build your own credit.
In order to qualify for loans, you have to work at getting a score. Opening a new credit card, even with a small initial credit limit, or making small purchases on credit are good places to start. Just be sure to make all payments on time and not to carry a balance on those cards. Establishing a good credit score from having no credit history is a matter of starting small and avoiding any of the mistakes listed above that will hurt your credit.
Having a credit score is essential if any time in the future you are wanting to rent an apartment, get approved for a major credit card, take out a loan on a car, or qualify for a mortgage. Also, it is possible you will not be able to get utilities (including a phone), insurance, or even a job without some sort of credit history. However, paying for a phone in installments and other smaller purchases like this can help you establish good credit.
To build your credit up carefully, there are a variety of other options to carefully consider. One example includes asking a parent or someone you trust to add you as an authorized user on one of their credit cards. That way, any activity on that card will appear on your credit report.
Other things you can do are to open a secure credit card (requires a cash deposit that serves as collateral), a student credit card (usually has a low limit), or a retail store credit card (typically doesn’t require a past credit history).
With any of these examples, payments must be made on time every month in order to build a positive credit history. Little by little, your credit score will rise higher and higher and you will be able to qualify for bigger loans over time. Small credit limits will be raised over time by the credit card company, and your credentials as a borrower will grow stronger over time.
If your credit score is currently low, there are other things you can do. Paying off credit card balances, for example, will reduce your debt-to-income ratio. Lenders are less likely to give loans to people who seem to have too much debt already. Paying off current debts will free up income for future loan payments and improve your scores. At the same time, you will save yourself a lot of money by not paying as much interest to credit card companies.
To wrap up the question of what’s a good credit score, anything over 670 qualifies to be in that category. Just remember, if you’re not quite there, you still have options! Having a good credit score means taking charge of your own credit. That means knowing what goes into a credit score and staying on top of each of those items. Raising your score will help you obtain better loan rates. This can save you thousands of dollars.
Visit Lift Credit for more information. Read our blog post about improving credit scores!